
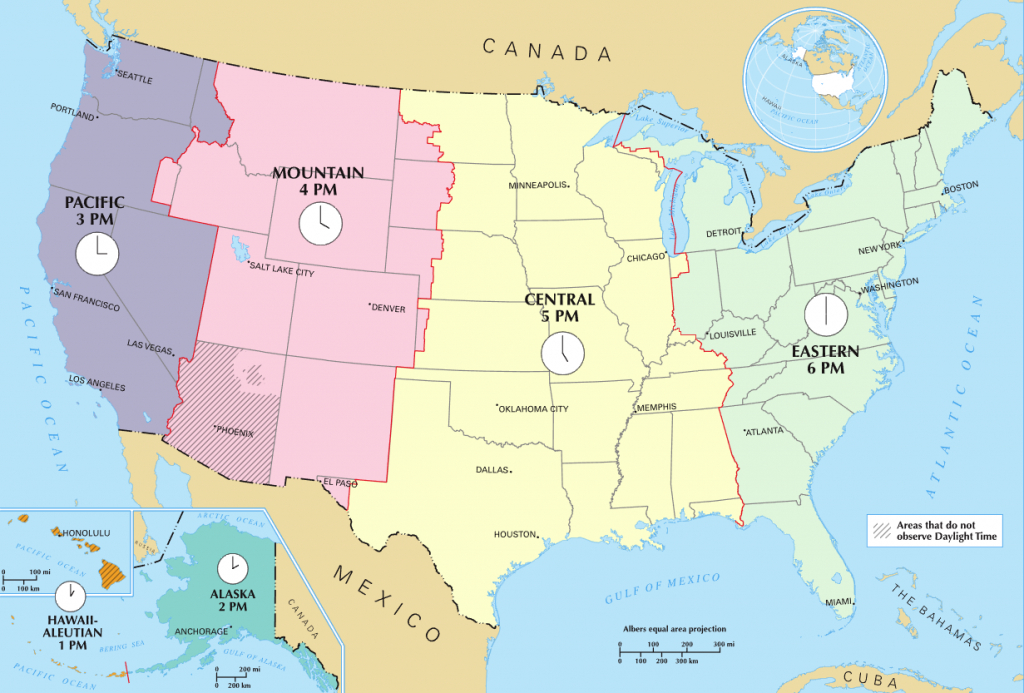
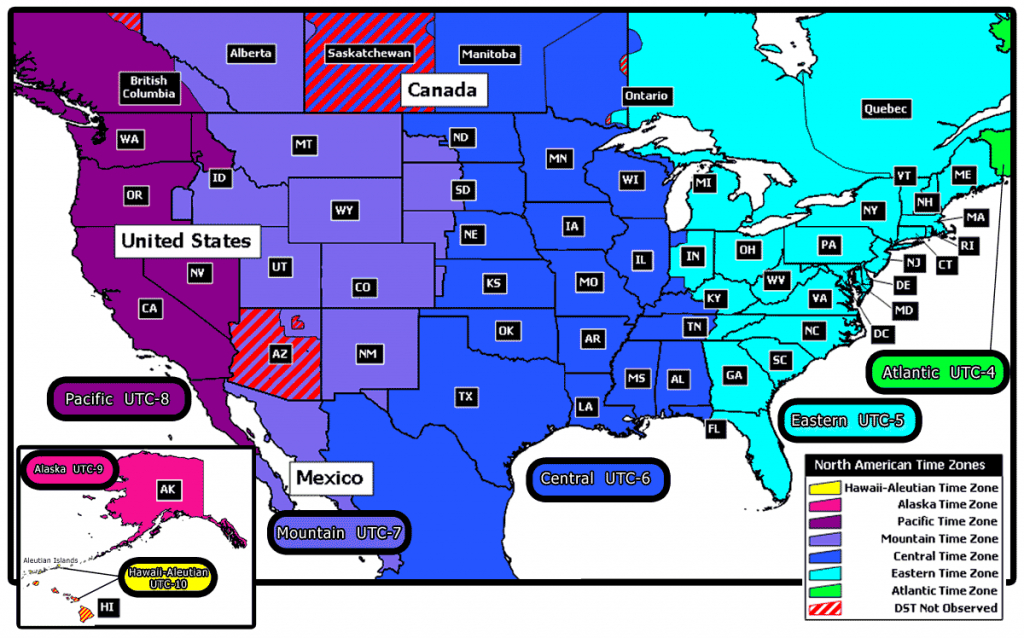
However, considering the size of the country, the amount of time zones is quite normal. The majority of them follow daylight saving time (DST) for approximately half a year starting from the spring months. The US is divided into six standard time zones. That’s not to mention half-hour time zones, similar to the old Amsterdam time, which ruled that Amsterdam was 20 minutes ahead of London. Australia, on the other hand, has three time zones. However, not all countries follow the same conventions: China, for instance, operates in one single time zone (CST). That line determines the rest of the time zones around the world. Time was standardised and a prime meridian was chosen as Greenwich, London (hence Greenwich Mean Time), with eight countries aligning including, France, Spain, Algeria and Togo.
In 1884, 26 countries met in Washington, DC, to attend the Meridian Conference.

Clocks display time from various time zones at Warsaw Stock Exchange, Poland, part of Central European Time. Time zones are pretty simple, right? In the EU, there are three standardised time zones: Western European Time in Ireland and Portugal, Central European Time, covering the bulk of the mainland such as Germany and Poland, and Eastern European Time, which includes Estonia, Finland, Lithuania, Romania, Bulgaria, Greece and Cyprus.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
